The Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) process has been designed using the principles set out in the British Geriatric Society CGA Toolkit for Primary Care Practitioners.
The process has been designed to dovetail with other aspects of care planning, Frailty Management, the Co-ordinated Care and Palliative Care Systems.
The CGA template is designed to show the key information which is already recorded. This is especially important when parts of the assessment are carried out by different members of an MDT.
How to Access
To access the Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment Template, either use the search bar in the lower left-hand corner or press F12, search for Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment CGA – CDRC.
Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment Template
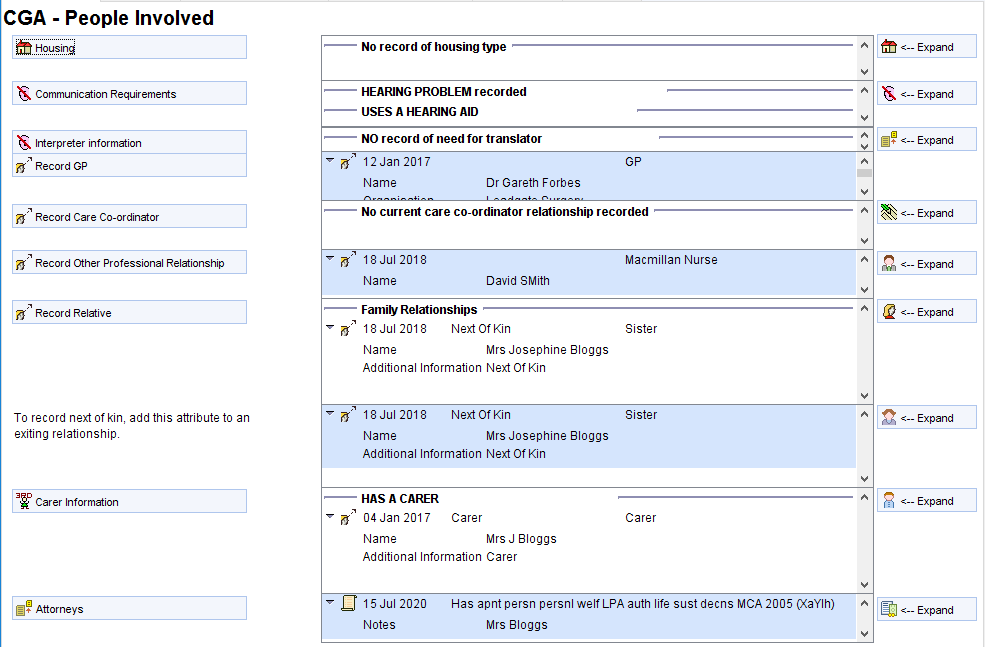
The CGA – People Involved Page allows the user to record important contacts including: named GP, care coordinator, other professionals, carers (formal or informal), relatives, next of kin, attorneys and other proxy decision makers.
The Assessment Page
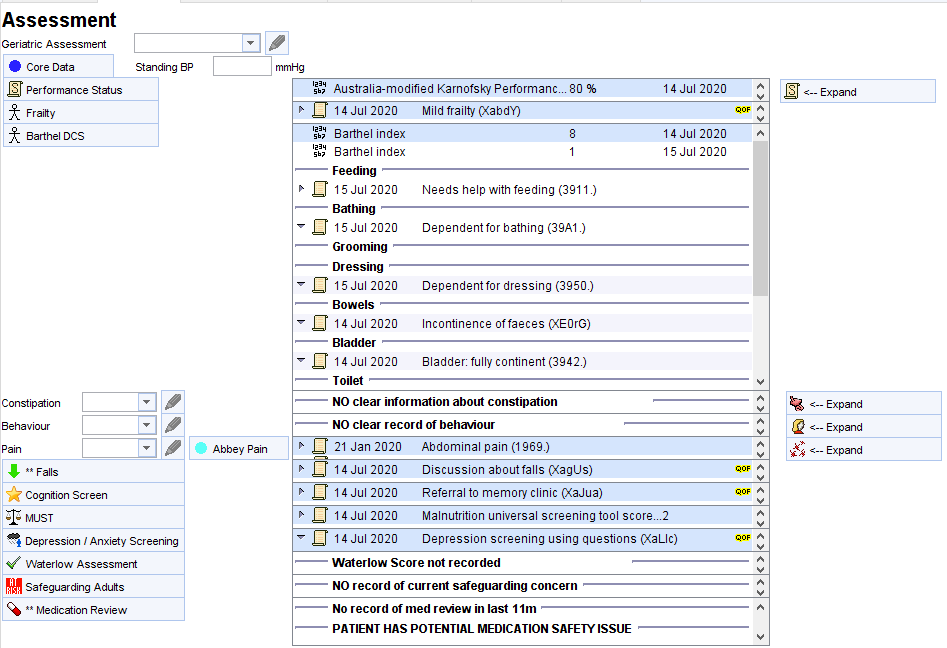
This page covers the key elements of the CGA assessment:
- Core data – e.g., height, weight, smoking, alcohol, pulse, BP.
- Performance status – users have the option to use WHO scale or modified Karnowski.
- Frailty – helps users diagnose and categorise frailty.
- Barthel – key ADLS, including continence.
- Constipation.
- Behavioural issues.
- Pain – with a link to the Abbey pain scale for those patients who can’t articulate well.
- Falls – allows recording of key information about falls and triage using the FRAT scoring tool.
- Cognition screening – using the 6 CIT test.
- Nutrition – using the MUST screening tool.
- Depression and anxiety screening using Whooley’s two questions and GAD2.
- Waterlow pressure assessment.
- Safeguarding concerns – displays information about potential safeguarding concerns and allows the patient to be added to the unit’s safeguarding register.
- Medication review – a comprehensive polypharmacy medication review system.
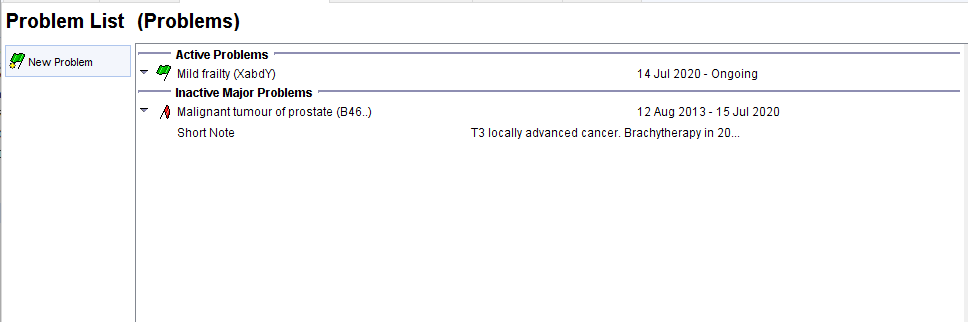
The Problem List Page (separate pages for the problem and summary functions to accommodate practices that use each of these systems to maintain their problem lists).
The Care Planning Page has the following information:
- SCR Consent – allows recording of consent/dissent for sharing via SCR, especially the enhanced SCR.
- Consent to share with others – a place to record which other individuals the patient is happy to share with e.g., relatives.
- Resuscitation – allows recording of resuscitation status and discussions as well as completion and creation of DNACPR forms using the deciding right guidance and forms.
- Preferred place of care and death.
- Other death wishes – including donor status, type of funeral.
- EHCP – allows creation of an Emergency Health Care Plan using the deciding right guidance and forms.
- Advance Decision – allows recording of ADRTs.
- Advance statement – Allows recording of advanced statement which might be simply documentation of the what the patient has expressed to the user or signposting to a more formal document.
- SPN – allows creation of a special patient note to send to the ambulance service to cover key information such as those in this list.
- Capacity Assessment/Best Interests – opens a checklist that guides the user through an assessment of capacity and best interests making decision as well as ensuring this is documented clearly.
- Goals/Health Needs – allows the recording of up to 8 health needs or goals, along with the action to be taken to foster this.
- Care Plan creation – allows the creation of a document (electronic or paper) that acts as a personalised care plan. This includes most of the information from the People Involved and Care Planning sections of the CGA template along with the problem list, medication and allergies. The patients goals are clearly set out.
![CGA - Care Planning
Change SCR Consent
Consent to Share Vvtth Others
Resusctation
ppc
PPD
Other death preferences
Advance Decision
Advance Statement
SPN (NE-AS" 11)
Capacity Assmt aest Interests
Goalsyeath Needs
Care Plan CreationyFeviewyDecIined
New Recall (Coordinated Care)
SCR Core data is shared (implied consent)
No clear record about sharing with specified 3rd parties
15 Jul 2020 Not for attempted CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) (Xazgc)
14 2020
Preferred place of care - care home CXaaYt)
14 2020
Preferred place of death: home (XaJ3g)
DCS Death Wishes view has no data for patient
Has EHCP
NO clear record of ADRT
2018
Has advance statement (Mental Capacity Act
SPN to Ambulance/111 service RECORDED
15 2020
Ambulance (Lla1xF)
Capacity Assessment MCAI MCA2
Health Needs/Goal/Action Planning
2005) (XaYIc)
Entered by
Finished by
FORBES,
FORBES,
20 Feb 2020 14:50
15 Jul 2020 14:43
[1 5 Jul 2020 1 4:43]
Expand
o Expand
- Expand
Expand
Expand
- Expand (current)
- Expand (all)
Health Need 1
Describe the health need
Goal
Action
When will it be reviewed?
Gareth (Dr) (General Medical Practitioner)
Gareth (Dr) (General Medical Practitioner)
Poor mobility
Able to walk with zimmer
Refer to physio
OCTOBER 2020
15 Jul 2020
Personal care plan completed (XaR82)
This patient is in the virtual ward OR GSF Amber or Red OR End of life
15 Oct 2020
Coordinated Care
Pending](https://cdrc.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/image-131.png)
