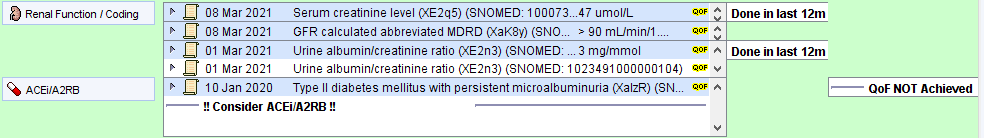
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is usually a clinical diagnosis in a patient with long-standing diabetes (>10 years) with albuminuria and/or reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in the absence of signs or symptoms of other primary causes of kidney damage.
Prevention of development/progression of DKD is helped by ‘standard’ interventions that also prevent macrovascular disease e.g.,
- Smoking Cessation
- BP Control
- Lipid Modification
- Hyperglycaemia Management
Specific interventions are also recommended for patients with diabetes and a persistently raised ACR>=3 (ACEi/A2RB and SGLT2i).
The following resources will help deliver these interventions:
Managing/ Preventing Diabetic Albuminuria
| Intervention | Workload | Realistic timeframe | Staff | Action | Search |
| Improving ACR testing uptake | Run batch searches at regular intervals e.g., fortnightly | Ongoing | Reception, care – coordinator | Contact patient by phone, SMS or email. | ACR Uptake for Diabetics – See below |
| Improve coding of albuminuria | Moderate amount of upfront work (often 5-10% of diabetic patients) followed by ongoing small amount of work | 1 month | GP, nurse practitioner, pharmacist | Review record and consider adding appropriate code | Albuminuria Coding for Diabetics – See below |
| Improving detection of significant albuminuria | Moderate amount of upfront work (often 5-10% of diabetic patients) followed by ongoing steady stream of work | 3 months | All staff | Review record and consider repeating ACR | Albuminuria Detection for Diabetics – See below |
| Improving management of diabetic albuminuria | (Usually) large amount of upfront work with smaller amount of ongoing work | 3 months | GP, nurse practitioner, pharmacist (? Suitable trained others e.g. pharmacy technician, practice nurse) | Consider prescribing ACEi/A2RB or recording reason why not | ACEi/A2RB Treatment for DKD – See below |
* NB – patients who have newly coded albuminuria may become eligible for ACEi/A2RB treatment, one of the diabetes QoF indicators. This process is best avoided towards the end of the QoF year.
ACR Uptake for Diabetics
Improving the uptake of ACR testing in patients with diabetes is an important step to improving Diabetes care and prevent of micro and macrovascular morbidity and mortality.
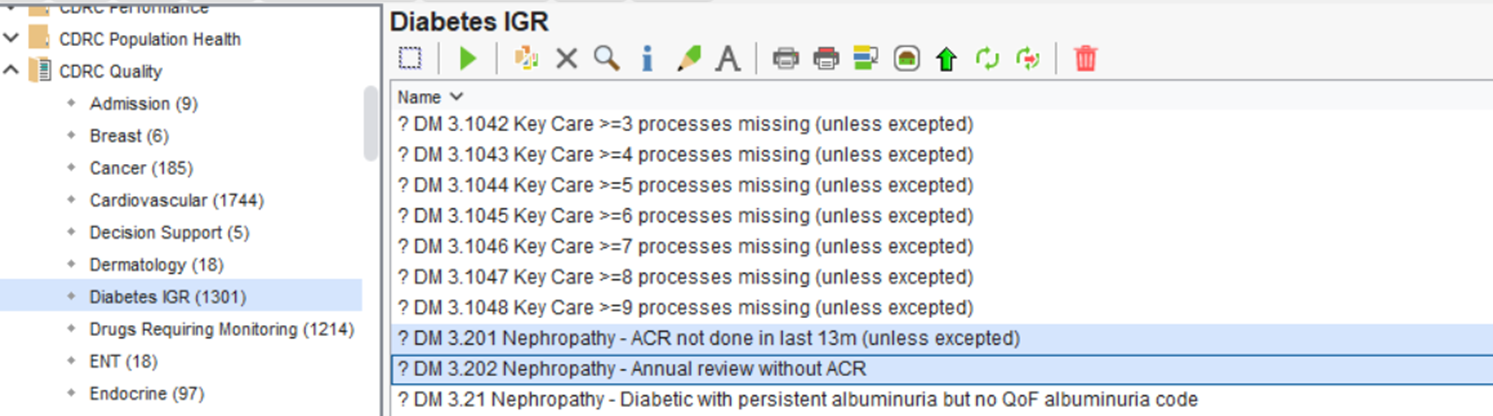
The two reports highlighted above identify diabetic patients who appear to be overdue ACR testing. The second report provides a more subtle approach and works well if added to an Automated Reporting batch that runs at regular intervals to report to reception or care-coordinators.
| Report Name | Returns | Actions |
| ? DM 3.201 Nephropathy – ACR not done in last 13m (unless excepted) | Patients with diabetes without a record of ACR in the last 13m | Consider contacting these patients to invite them to submit urine sample |
| ? DM 3.202 Nephropathy – Annual review without ACR | Patients whose diabetes annual review took place at least a month ago who haven’t yet submitted an ACR | Consider contacting these patients to invite them to submit urine sample. This is a good search to run on a regular (e.g. fortnightly) batch |
Patients can be contacted by phone, SMS or email.
Suggested text to use in the Communications Annexe
<forename> <surname>
Please could you drop in an early morning urine sample to the surgery. This is due as part of your regular check up.
Regards
Organisation Name inserted here
Albuminuria Coding for Diabetics
Definitions
Microalbuminuria – ACR persistently >=3 to 30 (at least 2 out of 3 samples over a few months)
Albuminuria/Proteinuria – ACR persistently >30 (at least 2 out of 3 samples over a few months)
Coding Issue
QoF only ‘recognises’ patients with diabetes as having microalbuminuria/albuminuria if they have one of the Snomed codes from the MAL (micoralbuminuria) or PRT (proteinuria) code clusters. The most appropriate codes from these clusters are shown below. QoF does not ‘count’ either ACR numeric results >=3 or CKD codes which confirm microalbuminuria e.g. CKD G3a A2 (although QoF does recommend proteinuria CKD codes such as CKD G3b A3)
These are the recommended codes to use for diabetic patients with persistently abnormal ACR results.
| Diabetes Type | ACR >3 | ACR >30 |
| Type 1 | Type 1 diabetes mellitus with persistent microalbuminuria | Type II diabetes mellitus with persistent microalbuminuria |
| Type 2 | Type II diabetes mellitus with persistent microalbuminuria | Type II diabetes mellitus with persistent proteinuria |
| Other diabetes | Diabetes mellitus with persistent microalbuminuria | Diabetes mellitus with persistent proteinuria |
The earliest code from these clusters will be shown in the renal panel of the Diabetes CDRC template.

The following reports will help to identify and manage these patients
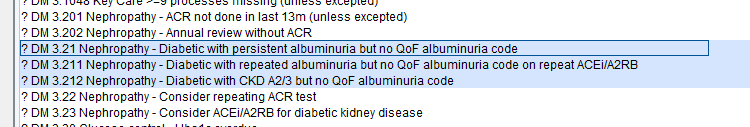
These reports can be found in the folder CDRC Quality > Diabetes IGR
| Report Name | Returns | Actions |
| ? DM 3.21 Nephropathy – Diabetic with persistent albuminuria but no QoF albuminuria code | Patients whose last 2 ACR results are >=3 but who do not have a code in the MAL or PRT clusters | Review record and consider adding relevant code from list above |
| ? DM 3.211 Nephropathy – Diabetic with repeated albuminuria but no QoF albuminuria code on repeat ACEi/A2RB | Patients who are already on an ACEi/A2RB who appear to have had repeated ACR results >=3 | Review record and consider adding relevant code from list above. NB this report will improve QoF performance. |
| ? DM 3.212 Nephropathy – Diabetic with CKD A2 but no QoF albuminuria code | Patients whose latest CKD code indicates they have significant albuminuria but who don’t have a code from the MAL cluster | Review record and consider adding relevant code from list above |
Albuminuria Detection for Diabetics
Definitions
Microalbuminuria – ACR persistently >=3 to 30 (at least 2 out of 3 samples over a few months).
Albuminuria/Proteinuria – ACR persistently >30 (at least 2 out of 3 samples over a few months).
Patients with an isolated raised ACR should have a repeat ACR measured to confirm or refute persistent abnormality.
This report will identify patients with diabetes who might have microalbuminuria/albuminuria who can be offered a repeat test.
This report can be found in the folder CDRC Quality > Diabetes IGR

| Report Name | Returns | Actions |
| ? DM 3.22 Nephropathy – Consider repeating ACR test | Patients whose last ACR result (at least two months ago) is >=3 who don’t have a code in the MAL/PRT clusters | Review record and consider requesting repeat ACR testing to confirm/refute albuminuria |
Patients can be contacted by phone, SMS or email.
Suggested text to use in the Communications Annexe
<forename> <surname>
Please could you drop in an early morning urine sample to the surgery. This is due as part of your regular check up.
Regards
Organisation Name inserted here
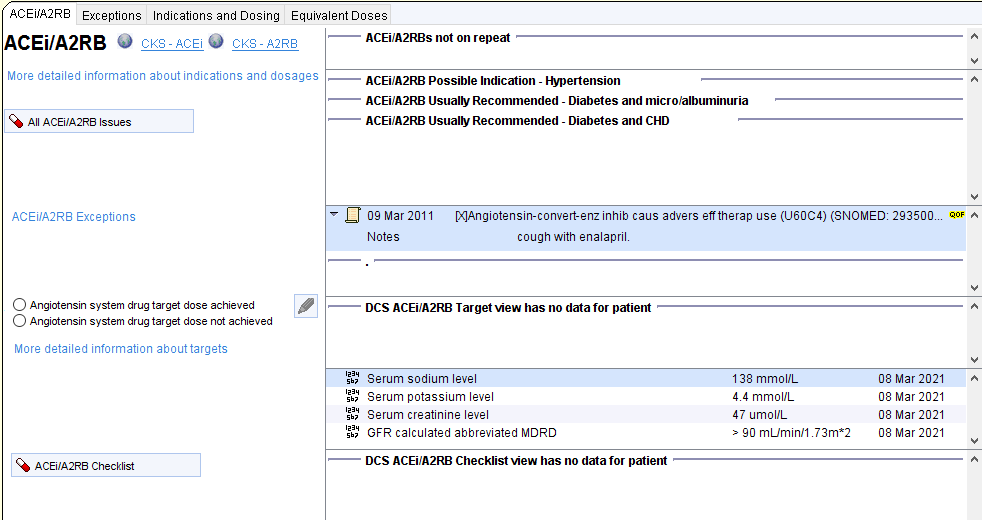
ACEi/A2RB Treatment for DKD
Renin-angiotensin system blockade offers significant benefits to patients with diabetes and persistent ACR>=3. Benefits include reductions in poor renal and cardiovascular outcomes.
One of the diabetes QoF indicators is based on RAS blockade for patients with diabetes and albuminuria.
This report will identify patients with diabetes who have coded albuminuria and who are not taking an ACEi/A2RB or don’t have a good reason why not. See Albuminuria Coding for Diabetics for coding issues (above).
This report can be found in the folder CDRC Quality > Diabetes IGR
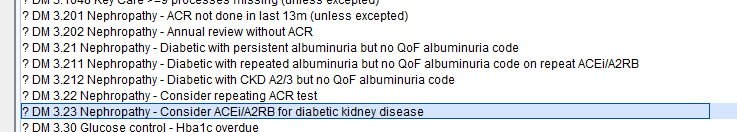
| Report Name | Returns | Actions |
| ? DM 3.22 Nephropathy – Consider repeating ACR test | Patients whose last ACR result (at least two months ago) is >=3 who don’t have a code in the MAL/PRT clusters | Review record and consider requesting repeat ACR testing to confirm/refute albuminuria |
‘Good reason why not’ is defined as:
Adverse reaction to ACEi (ever) OR ACEi declined/not indicated/not tolerated/contraindicated (last 12m)
AND
Adverse reaction to A2RB (ever) OR A2RB declined/not indicated/not tolerated/contraindicated (last 12m)
A warning about considering the need for ACEiA2RB will be displayed on the Diabetes CDRC template, along with the current QoF status. A link to the ACEi/A2RB template is available.