Initially created to support the implementation of a regional Atrial Fibrillation (AF) collaboration in the North East and North Cumbria region, the CDRC Precision AF suite of resources contains Reports, Templates and Targeted Alerts. These digital resources help to improve the rates of diagnosis and management of patients with Atrial Fibrillation and further support clinicians with safe anticoagulant prescribing and monitoring.
Accessing CDRC resources on SystmOne
To access the below resources you will need to be a member of the DCS group on SystmOne. To do this, please follow the instructions on the CDRC SystmOne Access webpage.
Atrial Fibrillation Screening
General screening for Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is not recommended. Screening is recommended for some patients with high risk conditions such as heart failure.
Screening At Annual Reviews
The CDRC Core Data Template includes a pulse check entry. This will ensure that people with LTCs are screened for AF.
Screening During Influenza Reviews
The Influenza Vaccination Template includes some quick action buttons to record pulse rhythm.
Additional Screening
CDRC can be configured to show alerts to prompt clinicians to screen for AF.
A Patient Status Alert (PSA) is available that displays the following icon to the right of the CDRC GMS icon:
Clicking on the link opens the Core Data Template to allow pulse rhythm to be recorded.
This PSA is currently built on a specification from Durham County Council:
- Over 75y
- Not of AF register
- Not on CHD, CKD3-5, diabetes, heart failure, stroke/TIA registers
- No pulse check in the last 50 months
This specification could be altered or customised for local areas if needed
The PSA is currently enabled for all practices in North Durham and DDES CCGs.
Atrial Fibrillation Quality Improvement Report Guidance
CDRC’s reports support the identification and management of patients with undiagnosed, un-coded and coded AF.
These reports are located in the folder CDRC Quality > Cardiovascular
One particularly useful strategy is to set these reports to run in a batch process (Automated Reporting) to go your cardiovascular/AF lead at regular intervals (6 to 12 monthly is a reasonable frequency).
| Report Name | Returns | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ? AF 2.1 Casefinding – Medication that might be for AF but no AF code | Patients on rate limiting calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, digoxin or amiodarone without obvious coded indication for these drugs. | Also likely to detect patients with other un-coded diagnoses such as hypertension and heart failure. NB – the drug to diagnosis reports in the table below find the same patients and are easier to use. |
| ? AF 2.2 Casefinding – AF potential indicator but no AF code | Patients with Read codes suggestive of AF but no QoF code e.g. H/O Atrial fibrillation. | Use the QoF CDRC Template (AF page – Non QoF AF Codes panel) to identify the relevant codes. |
| ? AF 2.3 Casefinding – Irregular pulse but no subsequent ECG | Patients who have an irregular pulse without a subsequent ECG. | Some of these patients will have erroneous entries of irregular pulse. |
| ? AF 2.4 Casefinding – AF marked as resolved | Patients who have previously had AF which is currently marked as resolved. | AF resolved should not be used for patients with paroxysmal AF who are not currently in AF. |
| ? AF 3.1 Case management – AF without CHADSVASc or possibly incorrect score | Patients with AF who do not have a CHADSVASc score or whose most recently recorded score may be incorrect. | Review patient and add/update score if appropriate. |
| ? AF 3.2 Case management – Consider Anticoagulation | Patients with AF and moderate or high stroke risk who are not anticoagulated and do have an expiring exception in the last year or a persistent exception. | Review the patient and consider anticoagulation or record exception if appropriate. |
A spreadsheet is available to support the drug to diagnosis audits Drug to Diagnosis Spreadsheet – Cardiac
| Report Name | Returns | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ? Drug to Diagnosis 002 – Antiarrhythmics without obvious indication | Also likely to detect other diagnoses such as heart failure, SVT, VT. | |
| ? Drug to Diagnosis 004 – Betablocker without obvious indication | Also likely to detect other diagnoses such as hypertension, heart failure, SVT, CHD. | |
| ? Drug to Diagnosis 005 – Calcium channel blocker without obvious indication | Also likely to detect other diagnoses such as hypertension, Raynauds, SVT, CHD. | |
| ? Drug to Diagnosis 008 – Anticoagulants without obvious indication | Also likely to detect other diagnoses such as VTE, mechanical heart valves. |
Atrial Fibrillation Performance Reports
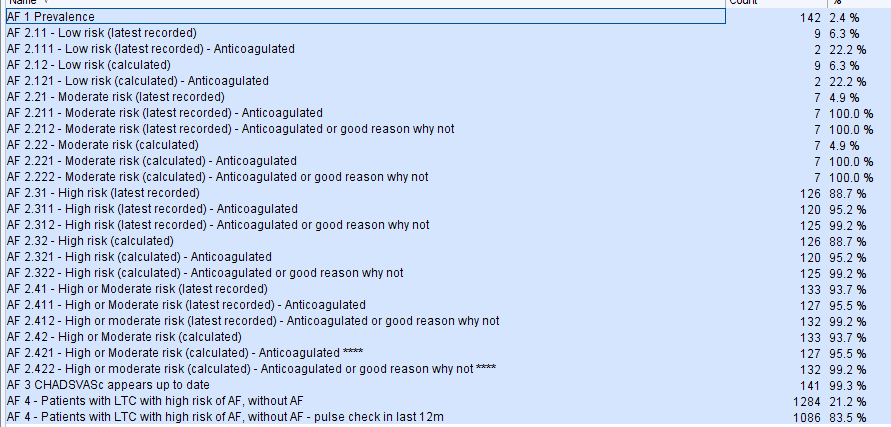
The AF Dashboard provides an overview of AF management at a particular unit or group of units.
These reports are in the folder CDRC Performance > Cardiovascular
Atrial Fibrillation QoF Support
Use the reports highlighted in the ‘Atrial Fibrillation Quality Improvement Report Guidance’ node above – this is because QoF payments are linked to prevalence so payments are higher if prevalence is higher.
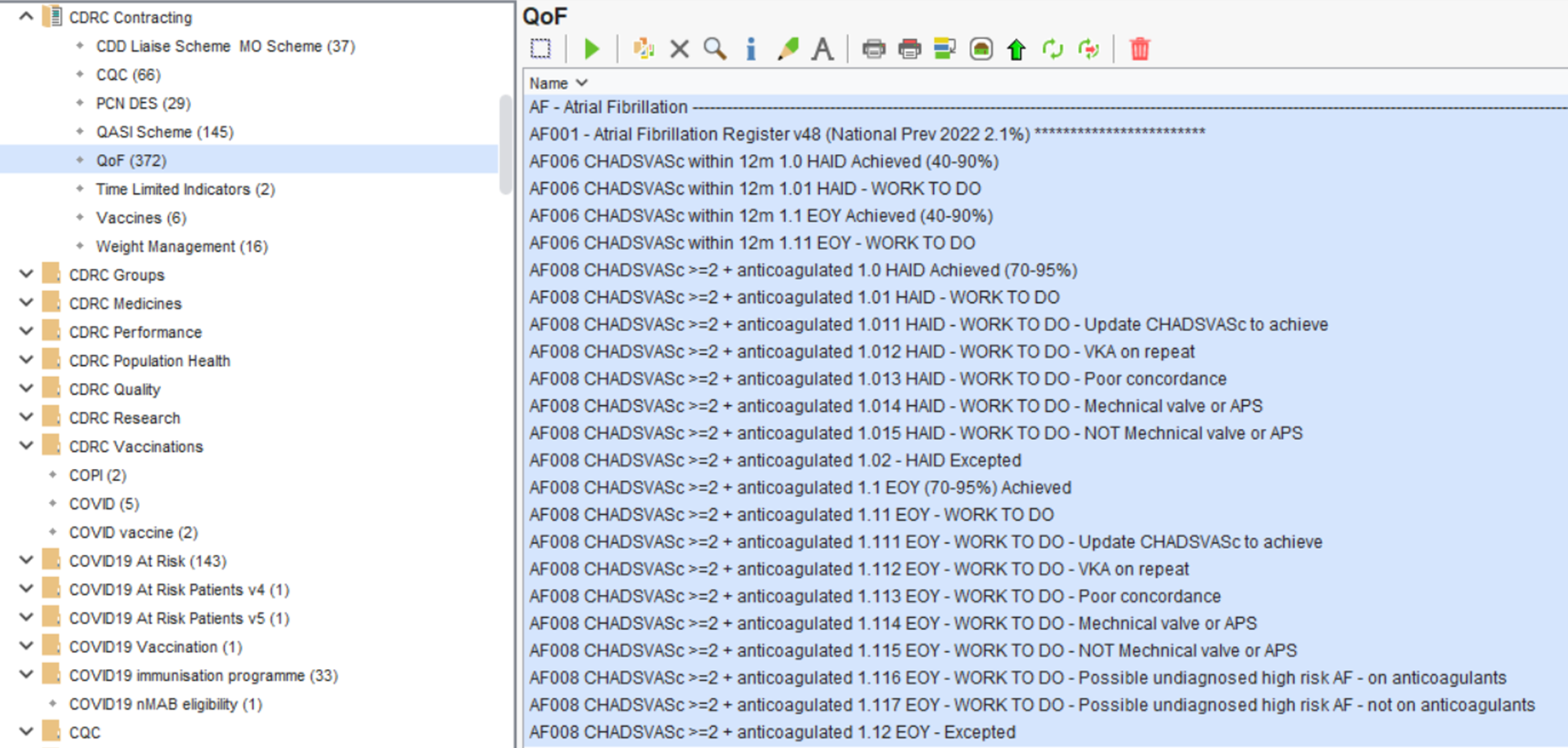
The following QoF reports are located in the folder CDRC Contracting > QoF
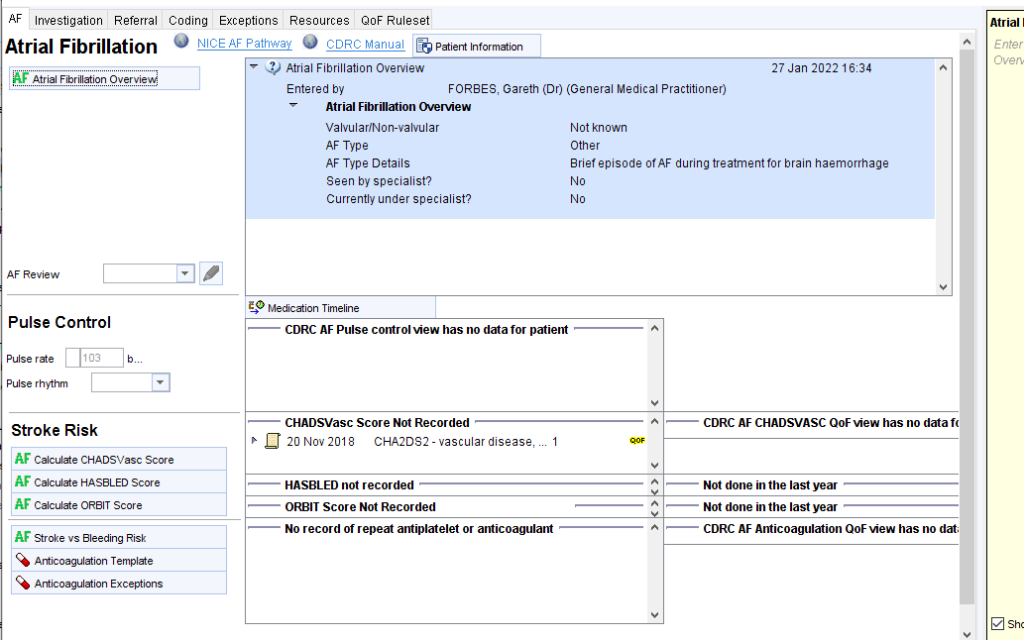
Atrial Fibrillation Template
The Atrial Fibrillation AF CDRC Template provides an overview of Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter management.
How to Access
In the lower left hand corner use the search bar, type in ‘Atrial Fibrillation AF CDRC’ and select the following template:
Alternatively, press F12 and search for ‘Atrial Fibrillation AF CDRC’, this will return the aforementioned template.
The Home Page will be used on most occasions.
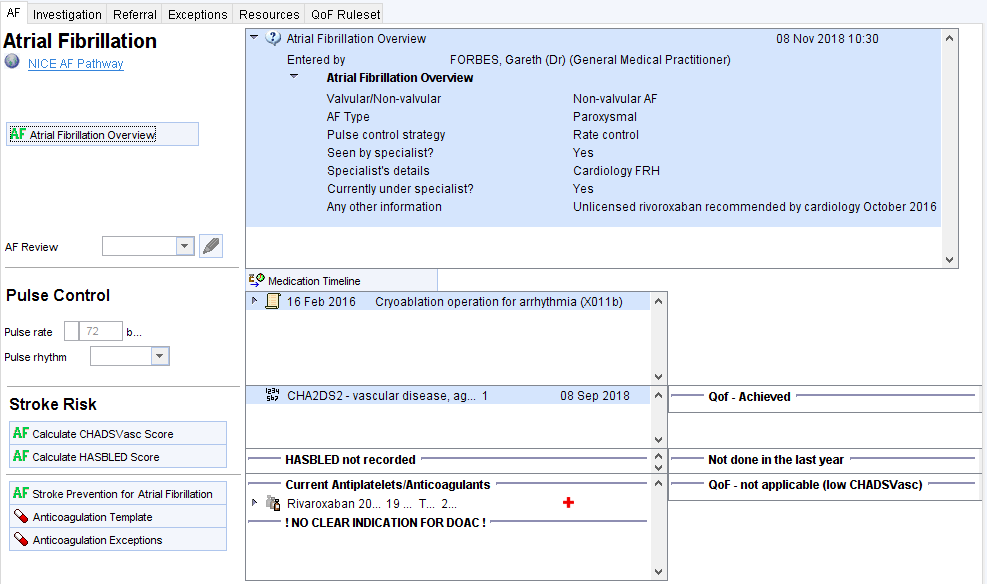
The top panel allows the user to provide a summary of AF management e.g. AF type, rate vs rhythm control status, who is currently involved in care, any narrative information.
The Pulse Control panel allows recording of current pulse rate and rhythm. The right hand box will show:
- Rate and rhythm control drugs (beta-blockers, rate limiting calcium channel blockers, digoxin, amiodarone and other antiarrhythmics such as flecainide and propafenone.
- Previous relevant cardiovascular procedures such as cardioversions and ablations.
The Medication Timeline button will display previous medication so it possible to see when previous treatments were started/stopped.
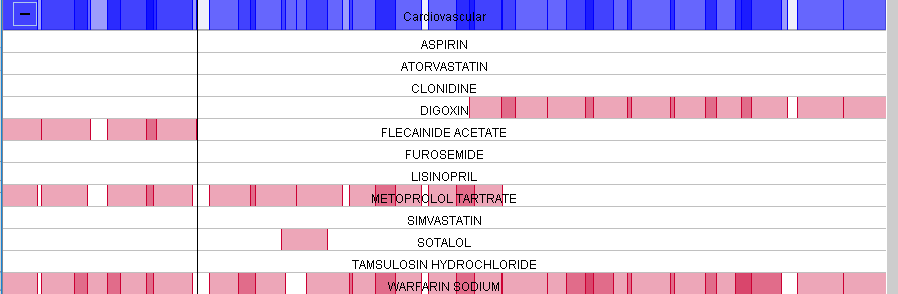
The Stroke Risk panel is divided into three columns:
- Column 1 – Links
- Link to CHADSVASc Calculator
- Link to HASBLED Calculator
- Link to Cardiovascular Network Guidance on anticoagulation decision making.
- Link to Anticoagulation template
- Link to information about Anticoagulation Exceptions
- Column 2 – Current information
- Current CHADVASc score. An alert is displayed if the current estimated CHADSVASc score is different to the most recently recorded score
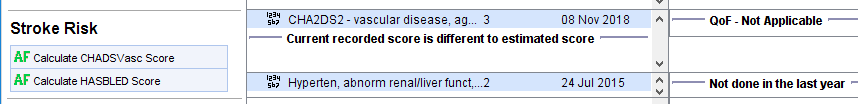
- Current HASBLED score
- Current antiplatelets/anticoagulants
- The following information is also displayed in this box:
- Recent expiring exception
- Persistent exception
- Evidence of poor concordance with anticoagulation treatment
- Evidence of poor warfarin control
- Evidence that DOAC treatment might need to change e.g. dose reduction/significant interactions.
- Current antiplatelets/anticoagulants

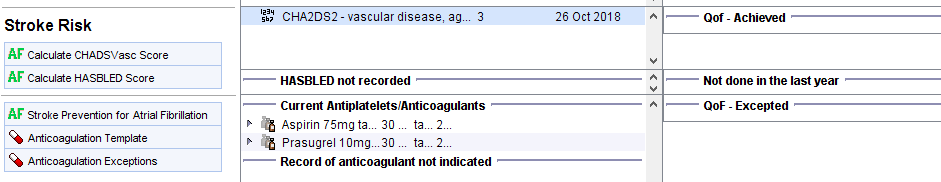
- Column 3 – performance indicators
- QoF AF006 indicator – CHADSVASc recorded
- HASBLED
- QoF AF007 indicator – patients with CHADSVASc >=2 treated with anticoagulation (example below)
CHADVASc Calculator
The CDRC system uses the system-wide TPP CHADSVASc calculator. However, there are some significant flaws in the TPP calculator (detailed below). This CDRC link will first run checks to look for these problems and provide warnings, allowing the user to adjust the CHADSVASc score if needed.
![CHADSVASc / CHAOS
This tool is only applicable to patients who are diagnosed with
either Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter
alculate @ CHADSVASc O CHAOS
C
A
S
V
A
Congestive heart failure (I pt)
Hypertensive (I pt)
D Age 75 (2 pts)
Diabetic (I pt)
Z] Stroke or TIA (2 pts)
Vascular disease (I pt)
Z] Age 65-74 (1 pt)
Z] Sex category female (I pt)
Score = 4 Save to Record
High Risk of Stroke
Consider oral anticoagulant](https://cdrc.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/image-5.png)

Potential Issues With TPP CHADSVASc Calculator
| Issue | Description | Effect | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Over diagnosis of hypertension | TPP calculator counts codes such as white coat hypertension and pregnancy induced hypertension as ‘currently hypertensive’ | Potential overestimate | Manually reduce score if the patient is not hypertensive |
| Over diagnosis of diabetes | TPP calculator counts codes such as metabolic syndrome as ‘currently diabetic’ | Potential overestimate | Manually reduce score if the patient is not diabetic |
| Underdiagnoses of heart failure, hypertension, stroke/TIA | TPP calculator does not include some codes for these conditions | Potential underestimate | Manually increase score if the patient has one of these conditions |
HASBLED Calculator
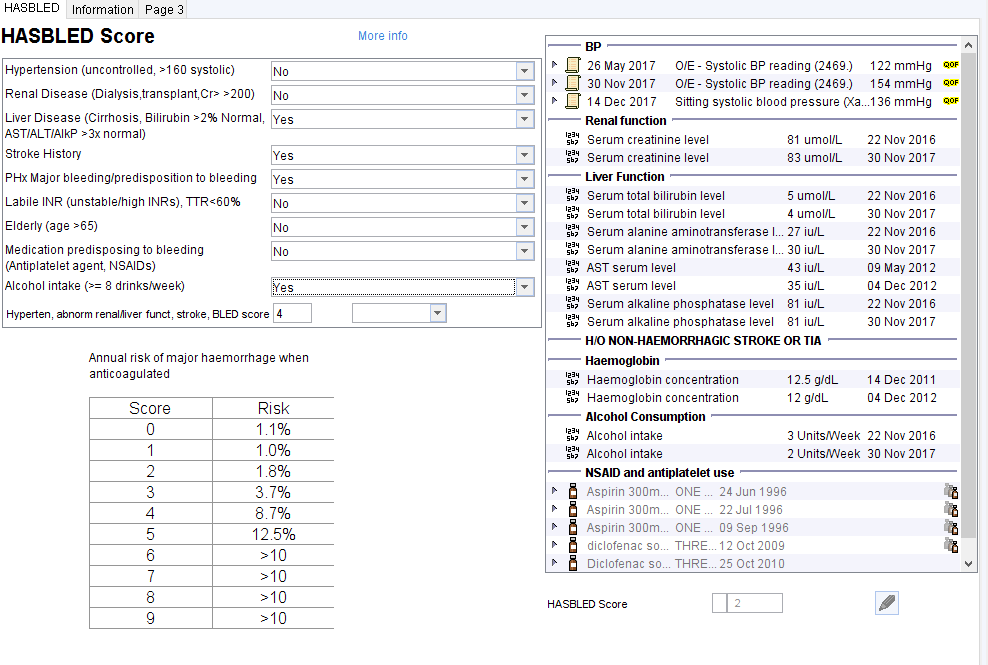
Stroke vs Bleeding Risk
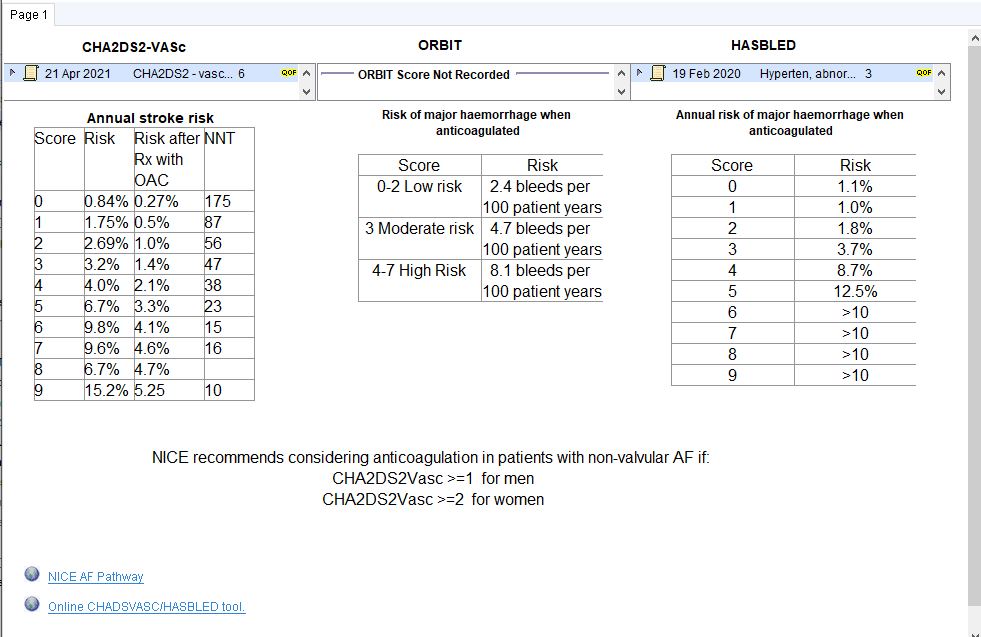
Anticoagulation Exceptions
This template shows anticoagulation exceptions.
‘Expiring’ exceptions are shown in the top half and ‘persisting’ exceptions in the lower half
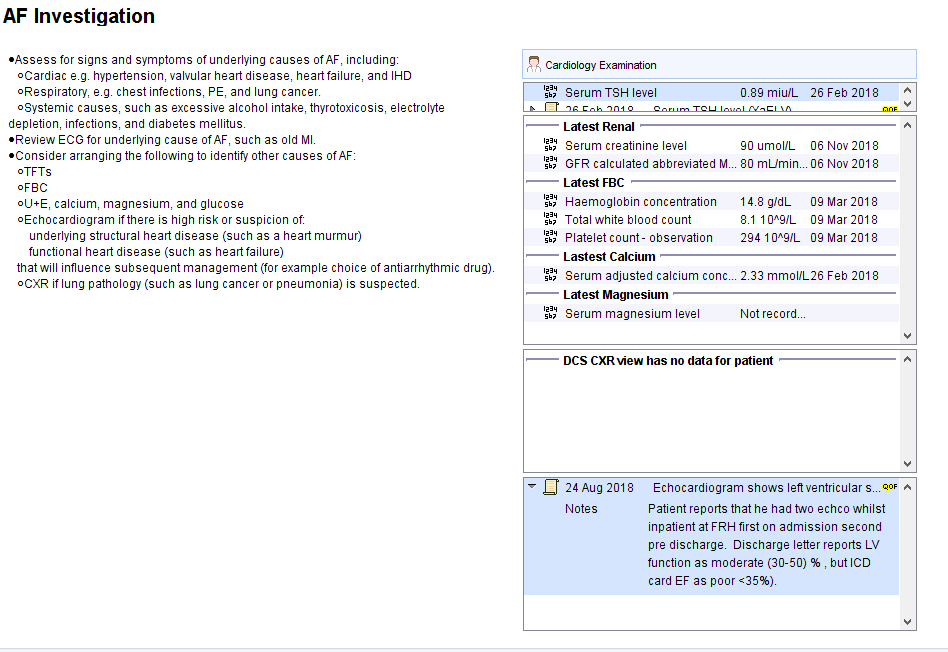
The Investigations Page page shows recommendation for testing and relevant information from the record.
The AF Referral Page page shows referral guidance.

Additional Resources
Atrial Fibrillation Resolved
Many patients with ‘resolved’ atrial fibrillation remain at increased risk of thromboembolic disease and should often be managed as if they have AF. The following guide for the management of people with past, transient or intermittent AF is put together by consensus of the North East and North Cumbria Cardiovascular Network.
| Paroxysmal AF | These patients usually retain a long term higher risk of stroke | Retain on the AF register and manage as AF unless instructed by a specialist – i.e. anticoagulation based on CHADsVASc vs bleeding risk assessment |
| AF related to hyperthyroidism | Long term risks of recurrence and thromboembolism are likely to be similar to background population | For patients whose only risk for AF is hyperthyroidism and where the AF resolves with successful treatment of the hyperthyroidism, mark the AF as resolved. Most commonly this affects young, otherwise healthy women. |
| AF and cardioversion/other procedures | Patients remain at significantly higher risk of thromboembolism from AF after successful ablation/cardioversion procedures | Unless otherwise advised by a specialist, do not mark these patients as AF Resolved. They should be managed as if they have AF. |
| AF after cardiac surgery | Transient AF is common after cardiac surgery such as CABG | Take advice from cardiology about whether these patients should be included on the AF register. |
| AF due to other stresses | Transient AF is not uncommon during other stresses such as non-cardiac surgery or infection. | Take advice from cardiology about whether these patients should be included on the AF register. |
The AF Template can help to record such reviews – in the Overview section
Opt-in Resources
For practices who have recently joined the DCS group on SystmOne, PSAs and Protocols will not be automatically active. You can choose the level of activation you would like; opt-in to all or resource specific CDRC resource PSAs and Protocols. Alternatively you can choose not to opt-in and only use the Reports and Templates.
If you would like to activate that following, or all, CDRC PSAs and Protocols, please email contact-cdrc@ahsn-nenc.org.uk
The AF Bundle of opt-in resources includes:
Patient Status Alert:
This PSA highlights whether the patient has AF.
Protocols:
| Protocol Title | Trigger | Action |
|---|---|---|
| AF Casefinding – Irregular Pulse AUTO S | Open patient with last pulse check irregular without subsequent ECG | Prompts user to check pulse rhythm +/- ECG |
| AF Casefinding – AF Potential Ind Added AUTO S | Triggers when a non-QoF potential AF indicator is added to a patient without AF (e.g. ECG:AF) | Prompts the user to consider coding AF |
| AF Casefinding – AF Potential Proc Added AUTO S | Triggers when a cardiac arrhythmia procedure is added to a patient without an obvious reason | Prompts the user to consider adding appropriate codes |
