Abnormal lipid profiles can be due to:
- Genetic abnormalities
- Single gene abnormalities such as familial hypercholesterolaemia
- Polygenic abnormalities such as common polygenic hypercholesterolaemia
- Secondary causes such as:
- Obesity / diabetes / NDH / metabolic syndrome
- Medication – antipsychotics, steroids, ciclosporin
- Anorexia
- Untreated hypothyroidism
- Alcohol excess
- A mixture of the two above
- Incorrect data entry
Abnormalities can be found in total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol and triglycerides.
A very common pattern is low HDL-C (<1 for men and <1.3 for women) and raised triglycerides (e.g. >2.3) which is seen in type 2 diabetes, obesity and the metabolic syndrome.
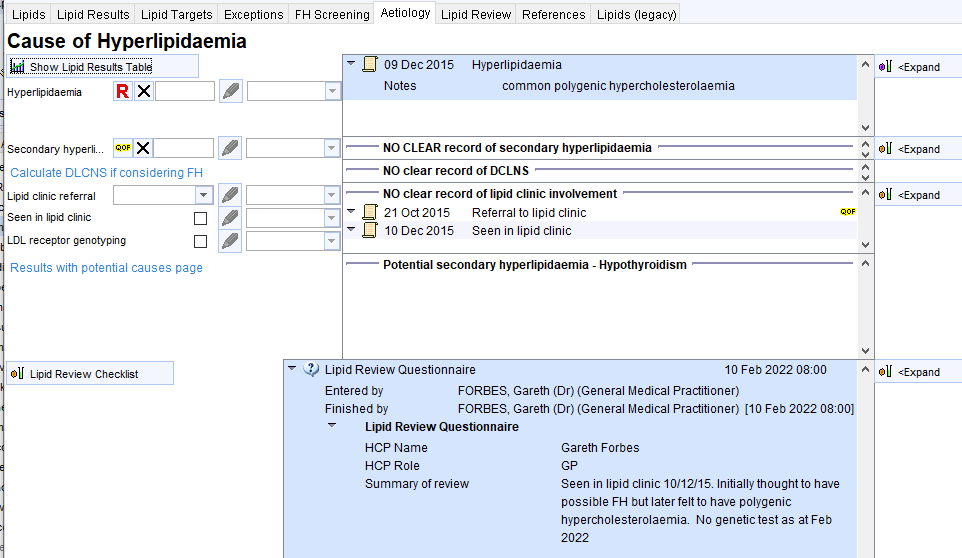
The Aetiology page of the Lipid Details Template can help show relevant information.
The upper part of the page allows coding of previous entries of: hyperlipidaemia codes; secondary hyperlipidaemia codes; previous DLCN scores; previous involvement with lipid clinics.
The lower part shows potential secondary causes of hyperlipidaemia and a space to record the narrative of the review.
There is a link to a page showing lipid results with links to relevant information such as BMI, HbA1c, antipsychotic scripts (second screenshot).
NB the Referral to lipid clinic code does not count for the IIF FH indicator – Referral for FH Assessment must be used.
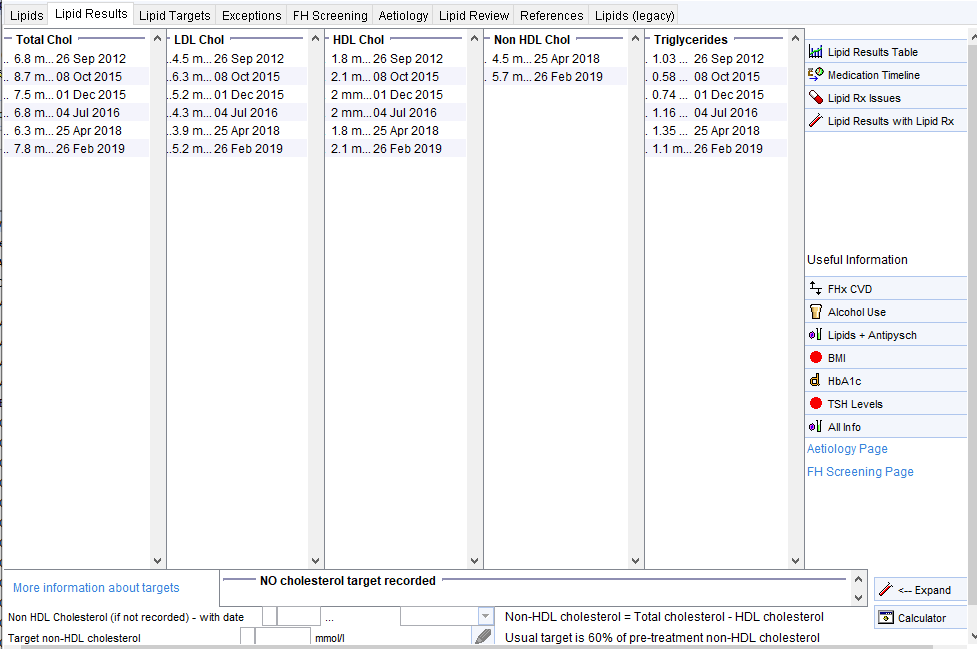
Some Examples – the following example show some common patterns of lipid abnormalities and how the template can help identify this.
Diabetes
This obese male in his 50 with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes has the common metabolic – syndrome pattern with low HDL-C and high triglycerides.
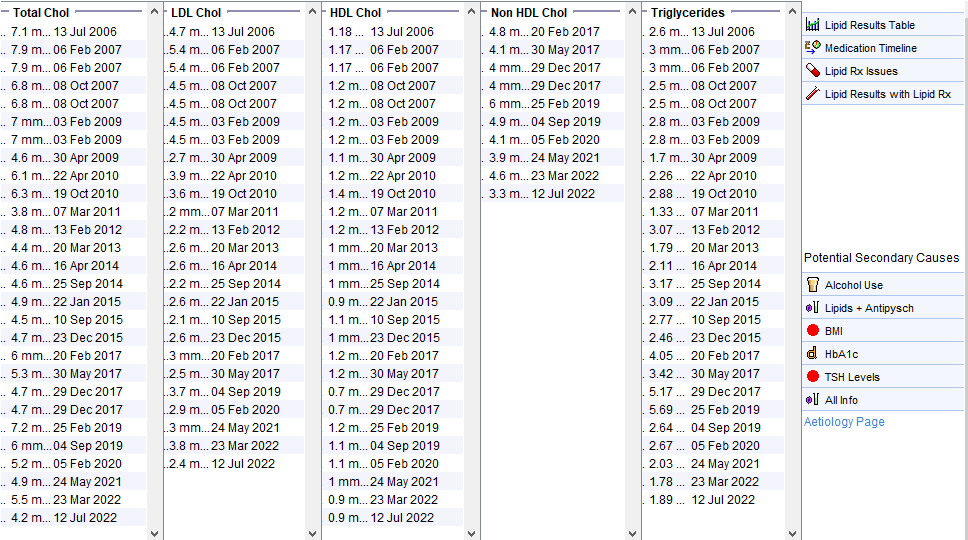
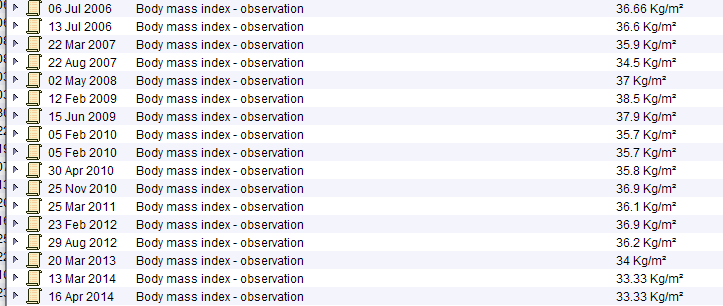
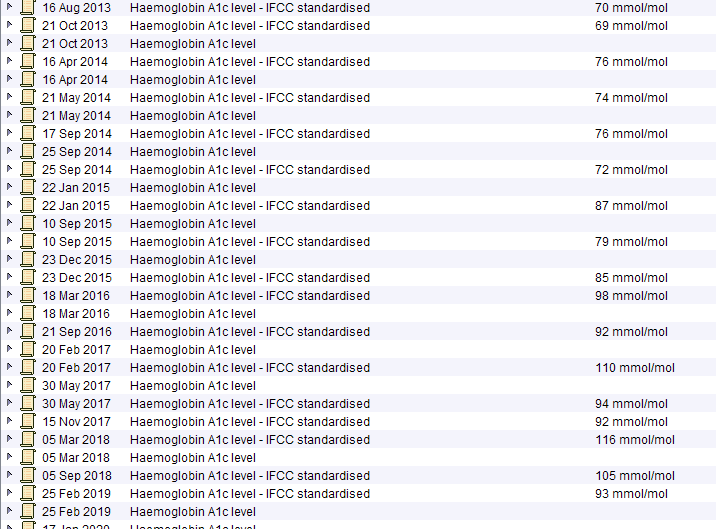
Obesity
Female patient in her 50s with a BMI in the range 38-42. Normal Hba1c. Note the raised triglycerides. The much more benign lipid profile from May 2019 was taken when she was on a low calorie diet – this makes an underlying lipid disorder very unlikely.
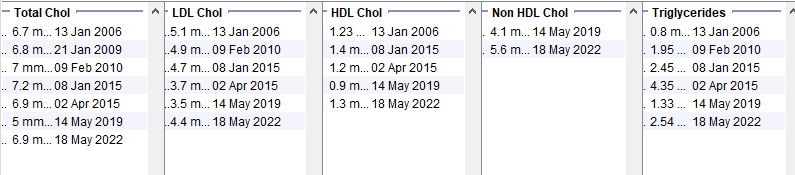
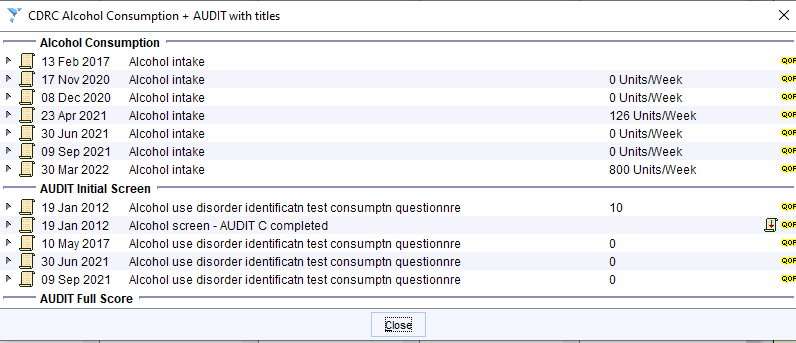
Alcohol Excess
Young male patient with BMI >30, normal HbA1c. Note low HDL and high triglyceride levels. The results are likely to be secondary to the very high alcohol consumption.
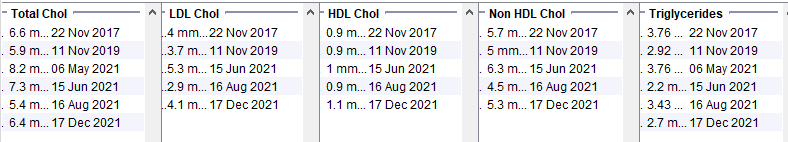
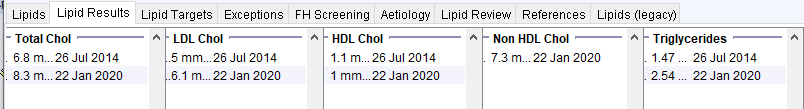
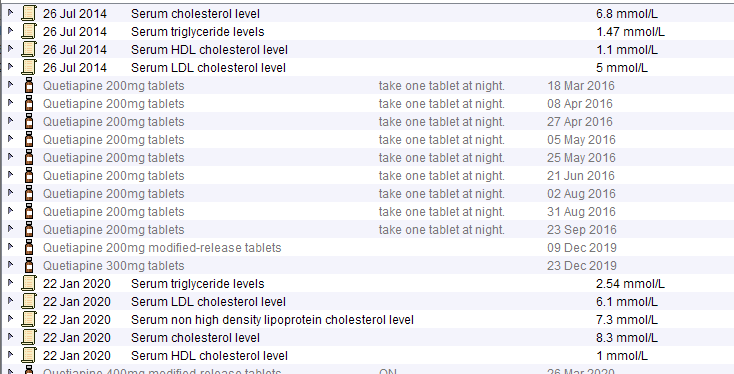
Antipsychotic Use
Young male patient with BMI ~32, HbA1c 42 and low alcohol consumption. The initial lipid profile is unfavourable – probably due to obesity and NDH. The lower panel shows how the lipid profile worsens significantly once antipsychotics are started.
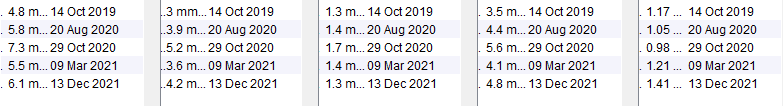
Isolated Abnormalities
Young female patient with low BMI and an isolated raised cholesterol which dropped back down again without any treatment. This is very unlikely to be due to an underlying lipid disorder. Low BMI and anorexia can be associated with abnormal lipid readings.

Familial Hypercholesterolaemia
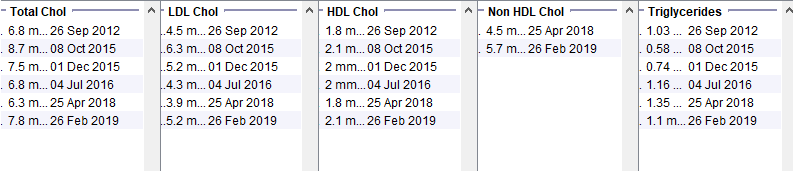
Female in her 50s with well controlled type 2 diabetes from the early 2010s. BMI 30-33. Family history of premature heart disease. Note that at the time of the very high cholesterol, the HDL is not low and the triglycerides are not high. Even though there are obvious secondary causes of hyperlipidaemia, the timing and the pattern of the lipid abnormality suggest further assessment is needed.
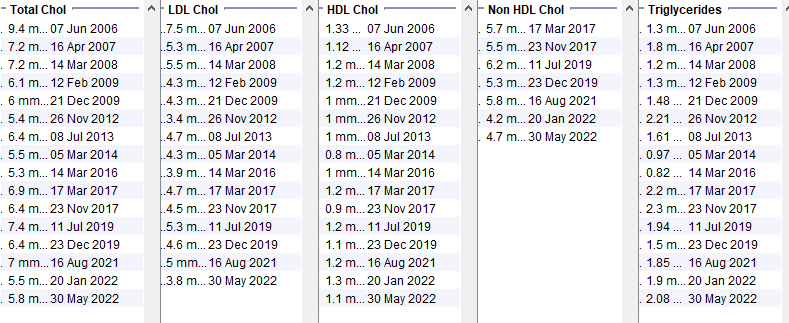
Use the Screening for Familial Hypercholesterolaemia page to calculate the Dutch Lipid Clinic Network score. Use local referral criteria to decide which patients need to be referred.
Polygenic Hypercholesterolaemia
Female in her 60s. Normal BMI and Hba1c. Strong family history of CVD but not premature CVD. High HDL and low triglycerides makes secondary causes of hyperlipidaemia unlikely. Assessed by lipid clinic and felt to have common polygenic hyperlipidaemia.